一、为什么重写了equals要重写hashcode?
有这么一个场景,当用户登录时,来了两个user,有name和age,并且还有手机号,手机号相同的我认为是一个用户。那么我们很容易得到以下代码:
import java.util.HashMap; public class MockLogin { static class User { public int age; public String name; public String mobile; public User( String mobile,int age, String name) { this.age = age; this.name = name; this.mobile = mobile; } } public static void main(String[] args) { //小灰灰登录 User xhhFirstLogin = new User("123456",21, "xiaohuihui"); //这里我想记录小灰灰是否登陆过 HashMap<User,Boolean> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put(xhhFirstLogin,true); //小灰灰第二次登陆来了,如果登陆过,我就把之前登陆信息给他,不再次登陆 User xhhSecondLogin = new User("123456",21, "xiaohuihui"); boolean b = map.containsKey(xhhSecondLogin); //看是否登陆过 System.out.println(b?"登陆过":"没有登录"); } } 但实际运行结果是:
没有登录 聪明的你一定看出来了,你没有重写equals啊,怎么判断手机号相等是同一个对象,好,那我们重写一下equals:
public class MockLogin { static class User { public int age; public String name; public String mobile; public User( String mobile,int age, String name) { this.age = age; this.name = name; this.mobile = mobile; } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; User user = (User) o; return Objects.equals(mobile, user.mobile); } } public static void main(String[] args) { //小灰灰登录 User xhhFirstLogin = new User("123456",21, "xiaohuihui"); //这里我想记录小灰灰是否登陆过 HashMap<User,Boolean> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put(xhhFirstLogin,true); //小灰灰第二次登陆来了,如果登陆过,我就把之前登陆信息给他,不再次登陆 User xhhSecondLogin = new User("123456",21, "xiaohuihui"); boolean b = map.containsKey(xhhSecondLogin); //看是否登陆过 System.out.println(b?"登陆过":"没有登录"); } } 重写完之后的结果:
没有登录 还是没有登录。那么问题究竟出在哪里了呢?既然是containsKey返回的false,我们就去看看containsKey是怎么写的吧
public boolean containsKey(Object key) { return getNode(key) != null; } 接着往下找:
/** * Implements Map.get and related methods. * * @param key the key * @return the node, or null if none */ final Node<K,V> getNode(Object key) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n, hash; K k; if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (first = tab[(n - 1) & (hash = hash(key))]) != null) { if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node ((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return first; if ((e = first.next) != null) { if (first instanceof TreeNode) return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key); do { if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return e; } while ((e = e.next) != null); } } return null; } 哦吼,这么多代码,关掉你的文章,休息一下。秋冬马爹,其实这里面只有一个行我们是需要注意的:
hash = hash(key));//根据key算出来的hash if (first.hash == hash && //对比第一个节点的hash值 ((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) //如果key和第一个节点的key相同或者(key不等于空并且相等) return first; 我们知道hashmap是一个拉链式的hash结构: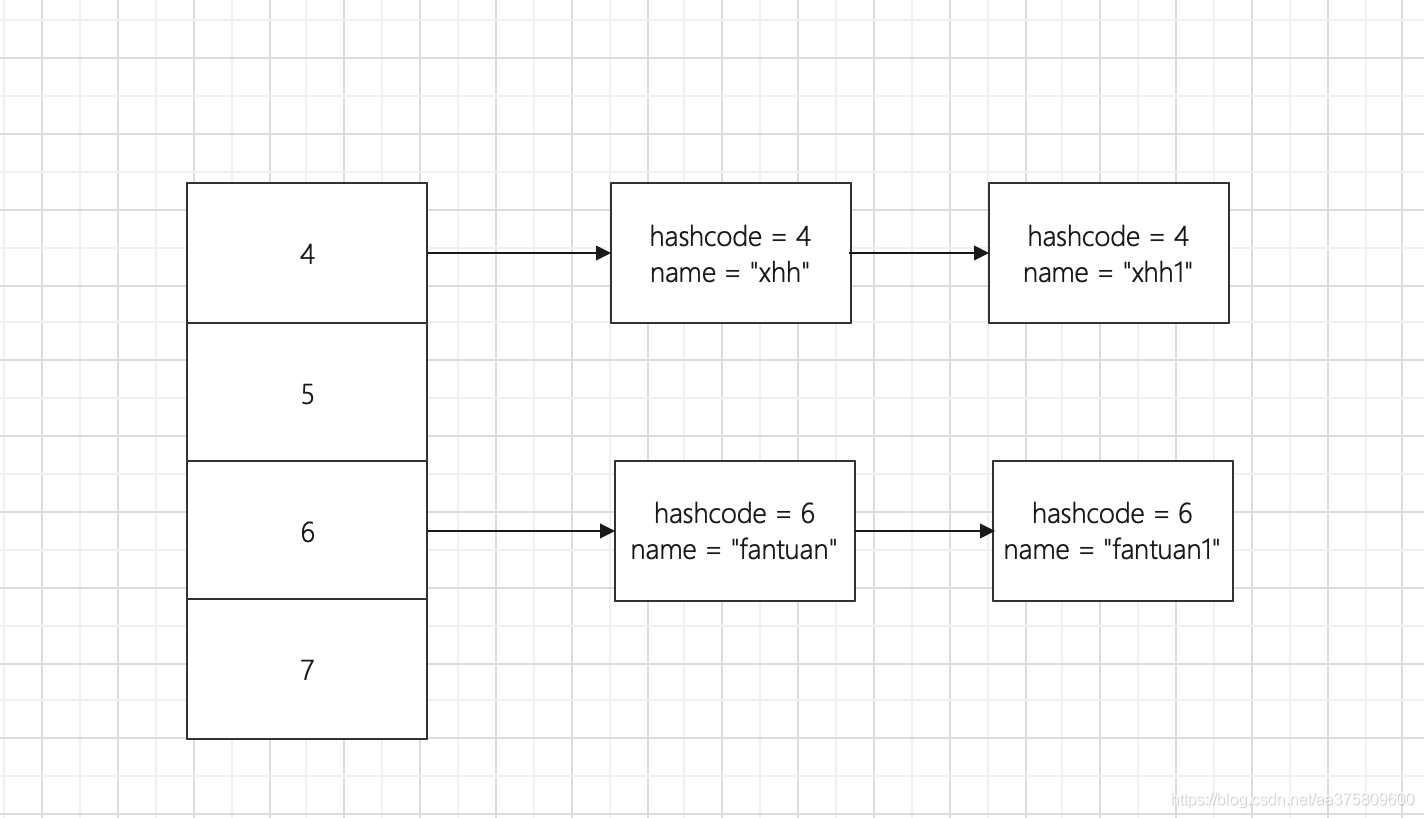
containsKey是先找到hashcode,然后再来对比是否相等的。那么我们很容易得到猜想,是不是刚才hashcode不一样,导致的containsKey返回了false。我们先来打印一下hashcode:
.... boolean b = map.containsKey(xhhSecondLogin); System.out.println("fcode = "+xhhFirstLogin.hashCode()+" scode = "+xhhSecondLogin.hashCode()); 看一下执行结果:
fcode = 1704856573 scode = 705927765 没有登录 果然,是hashcode导致了我们containsKey函数的失败。那我们先简单的处理一下,让他们相等:
public User( String mobile,int age, String name) { this.age = age; this.name = name; this.mobile = mobile; } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; User user = (User) o; return Objects.equals(mobile, user.mobile); } @Override public int hashCode() { return 1; } } 在user类增加hashcode方法,返回固定值1,我们再跑一下运行结果:
fcode = 1 scode = 1 登陆过 这时真的相等了,当然hashcode = 1这是为了做测试,工程化落地时,我们还是用hashcode标准方法吧:
@Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(age, name, mobile); } 我们认为,当他所有成员属性一样时,那就是一个对象,再次跑结果:
fcode = -679329960 scode = -679329960 登陆过 技术总结:
-
hashcode是一种快速定位到拉链法hash表数组位置索引的一个值,根据key算出来。
-
hashcode重写主要是为了解决对象在hash表中当key时,equals相等,但是hashcode不相等,导致containsKey错误返回的问题
贴一下最后的源代码:
package com.android; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Objects; public class MockLogin { static class User { public int age; public String name; public String mobile; public User( String mobile,int age, String name) { this.age = age; this.name = name; this.mobile = mobile; } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; User user = (User) o; return Objects.equals(mobile, user.mobile); } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(age, name, mobile); } } public static void main(String[] args) { //小灰灰登录 User xhhFirstLogin = new User("123456",21, "xiaohuihui"); //这里我想记录小灰灰是否登陆过 HashMap<User,Boolean> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put(xhhFirstLogin,true); //小灰灰第二次登陆来了,如果登陆过,我就把之前登陆信息给他,不再次登陆 User xhhSecondLogin = new User("123456",21, "xiaohuihui"); boolean b = map.containsKey(xhhSecondLogin); System.out.println("fcode = "+xhhFirstLogin.hashCode()+" scode = "+xhhSecondLogin.hashCode()); //看是否登陆过 System.out.println(b?"登陆过":"没有登录"); } } 热门文章
- 中国动物疫苗厂家排名前十有哪些(动物疫苗有哪些大厂家)
- 宠物商品品牌排行前十(宠物产品品牌排行榜)
- 动物防疫站举报电话(动物防疫站举报电话号码)
- Clash最佳梯子 | 4月8日22.9M/S|免费Shadowrocket/Clash/SSR/V2ray订阅节点地址
- 宠物领养中心在哪里(宠物领养中心官网)
- 一、重写了equals为什么还要重写hashcode
- 素数最多为n
- Clash最佳梯子 | 4月22日22.5M/S|免费SSR/V2ray/Shadowrocket/Clash订阅节点地址
- Clash最佳梯子 | 4月15日21M/S|免费Shadowrocket/Clash/V2ray/SSR订阅节点地址
- Clash最佳梯子 | 4月2日20.8M/S|免费Shadowrocket/SSR/V2ray/Clash订阅节点地址